What is the result of the general acceptance of liberal constructionist view in the United States? The liberal constructionists view has dominated and federal power has grown. What are the two Executive Powers given only to the Senate? Make treaties and appoint ambassadors.
What is a liberal construction quizlet?
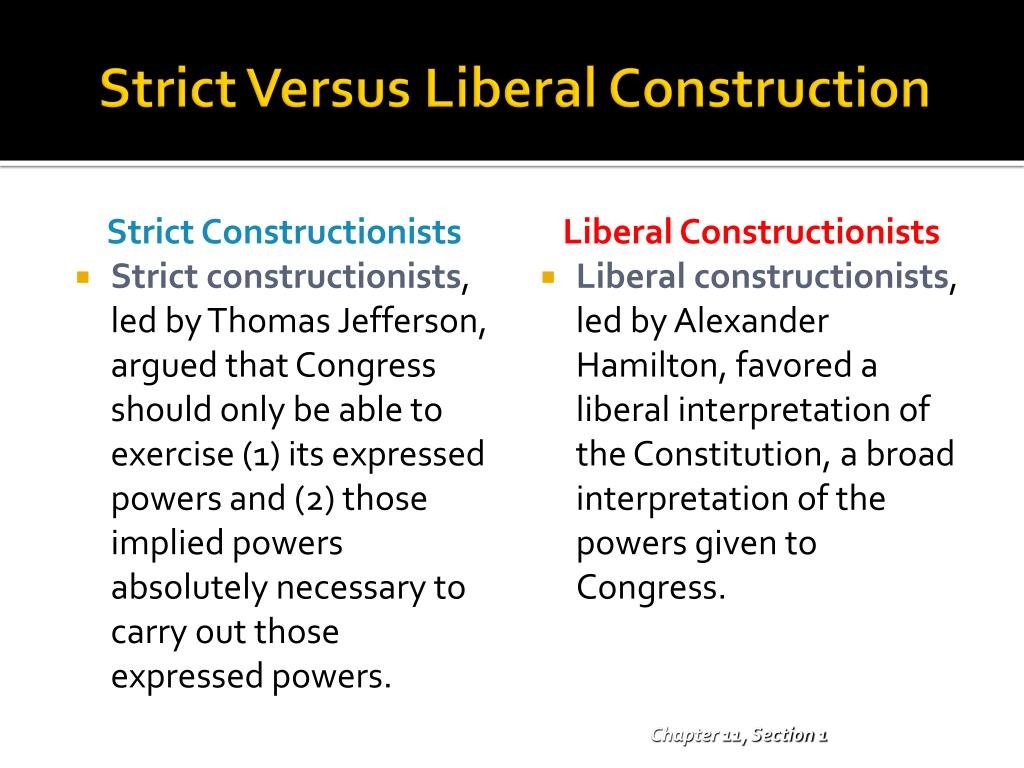
Liberal Constructionist. One who argues a broad interpretation of the provisions of the Constitution, particularly those granting powers to the Federal Government.
What is a value of the liberal constructionists?
Liberal constructionists believe that the Constitution must bed interpreted broadly, with an eye toward change. a. That belief has extended the powers of the Federal Government far beyond the plans of the original Framers of the Constitution.
What was the liberal construction attitude toward implied powers?
Liberal constructionists hesitated to use implied powers. Thomas Jefferson was a liberal constructionist. Liberal constructionists was linked to a strong National Government. Implied powers are those reasonably deduced from the expressed powers.
What is liberal constructionism?
Liberal constructionists believe that the Constitution must bed interpreted broadly, with an eye toward change. a. That belief has extended the powers of the Federal Government far beyond the plans of the original Framers of the Constitution.
Who believed in a strict interpretation of the Constitution?
Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson favored a strict interpretation of the Constitution, which he interpreted as forbidding everything it did not expressly permit. In contrast, Hamilton favored a loose interpretation.


TRANSCRIPT OF PRESIDENT TRUMP’S INDEPENDENCE DAY ADDRESS AT MOUNT RUSHMORE, JULY 3, 2020
— Team Trump (Text TRUMP to 88022) (@TeamTrump) July 3, 2023
The Story of America Makes Everyone Free
We gather tonight to herald the most important day in the history of nations: July 4th, 1776.
At those words, every American heart should swell…
What does strict construction mean quizlet?
Strict Constructionist. a person who interprets the Constitution in a way that allows the federal government to take only those actions the Constitution specifically says it can take.
Frequently Asked Questions
What did strict constructionists believe?
A strict constructionist is someone who believes that the text of the Constitution is not open to interpretation and that the words in the Constitution are literal. This philosophy is usually associated with the federal judiciary regarding cases that involve Constitutional matters.
What does the loose construction interpretation of the Constitution refers to?
The loose construction interpretation of the Constitution refers to the notion that. in carrying out its duties, the central government can take any measure not specifically prohibited by the constitution.
What were the five issues involved in the ratification debate?
5 Issues at the Constitutional Convention. When the 55 delegates gathered in Philadelphia to revise the Articles of Confederation, there were several major issues on the agenda to discuss including representation, state versus federal powers, executive power, slavery, and commerce.
Did anti federalist favor a strict or loose interpretation of the Constitution?
People who wanted a strict interpretation of the constitution were generally anti federalist and whose viewpoints were represented by Thomas Jefferson. The loose constructionists were people who desired a strong central government with less power to the states.
Did Hamilton or Jefferson believe in a loose interpretation of the Constitution?
Thus, Hamilton believed the best way to cultivate and preserve a republican form of government was to operate on a loose interpretation of the Constitution, predicated on the Necessary and Proper Clause (often referred to as the Elastic Clause), which would better fortify political freedoms for posterity. 1.
What is the loose interpretation of the Constitution quizlet?
The Loose interpretation states that the Federal government can do what is good for the country even if the Constitution doesn't explicitly allow it, but the Strict interpretation states that the Federal government can only do what the Constitution says it can do.
A person who favors a loose construction of the consitution would also dowhich of the following
A person who favors a loose construction of the Constitution would also do which of the following? 1.interpret the Constitution narrowly 2.take the same
Why was the ratification by Virginia and New York essential for the success of the Constitution?
New Hampshire became the ninth state to approve the Constitution in June, but the key States of Virginia and New York were locked in bitter debates. Their failure to ratify would reduce the new union by two large, populated, wealthy states, and would geographically splinter it.
Why was the ratification of Virginia and New York important?
The two most important states that had not decided by June 1788 were Virginia and New York, and without them in the Union the country would have been divided into parts: New England, the mid-Atlantic states, and the southern states.
Why was the ratification of the US Constitution important?
While the Constitution was not perfect, it created a stronger central government that included a Congress with the power to tax, a President who would act as the nation's chief executive, and a national court system.
Why was it crucial that New York and Virginia ratify the Constitution use details from the text to support your answer?
It was crucial that New York and Virginia ratify the constitution because they are the biggest states and the ratio between Anti Federalist in other states and Federalist in New york and Virginia. Having New York and Virginia could begin the ratification process.
Why was it important for New York and Virginia to ratify the Constitution quizlet?
Why was it especially important that New York and Virginia should ratify it? They were both populous and powerful; without their consent the Constitution would stand on shaky grounds.
Who constructed the Constitution?
Nationalists, led by James Madison, George Washington, Alexander Hamilton, John Jay, and James Wilson, almost immediately began working toward strengthening the federal government. They turned a series of regional commercial conferences into a national constitutional convention at Philadelphia in 1787.
Who was appointed to lead the Constitutional Convention?
George Washington
In 1787, George Washington was persuaded to attend the Constitutional Convention and subsequently was unanimously elected its president.
Who led the meeting to create the U.S. Constitution?
A More Perfect Union: The Creation of the U.S. Constitution
Robert Morris of Pennsylvania, the "financier" of the Revolution, opened the proceedings with a nomination--Gen. George Washington for the presidency of the Constitutional Convention. The vote was unanimous.Who came together to make the Constitution?
In all, 55 delegates attended the Constitutional Convention sessions, but only 39 actually signed the Constitution. The delegates ranged in age from Jonathan Dayton, aged 26, to Benjamin Franklin, aged 81, who was so infirm that he had to be carried to sessions in a sedan chair.
What was a name for supporters of the Constitution?
During the year-long debates over ratification, supporters of the Constitution called themselves Federalists; as a result, their opponents were known as Anti-Federalists.
What concepts are used in the US Constitution?
Additional Resources. Teaching Six Big Ideas in the Constitution - Students engage in a study of the U.S. Constitution and the significance of six big ideas contained in it: limited government; republicanism; checks and balances; federalism; separation of powers; and popular sovereignty.
What term most closely describes the form of government created by the Constitution?
The Constitution established a Federal democratic republic. It is the system of the Federal Government; it is democratic because the people govern themselves; and it is a republic because the Government's power is derived from its people.
Which amendment to the Constitution relates most closely to the concept of federalism?
Which of the following directly influenced the United States Constitution?
What are the three concepts of the Constitution?
The Principles Underlying the Constitution
Federalism aside, three key principles are the crux of the Constitution: separation of powers, checks and balances, and bicameralism.
FAQ
- In what way does the construction of a home for its presidents help the young nation to established
Jefferson played a major role in the planning, design, and construction of a national capitol and the federal district. In the various public offices he held,
- Who is known as the Father of the Constitution?
James Madison
James Madison, America's fourth President (1809-1817), made a major contribution to the ratification of the Constitution by writing The Federalist Papers, along with Alexander Hamilton and John Jay. In later years, he was referred to as the “Father of the Constitution.”- What is James Madison famous for?
Madison is hailed as the "Father of the Constitution" for his pivotal role in drafting and promoting the Constitution of the United States and the Bill of Rights. James Madison Jr.
- What was James Madison died?
James Madison's Montpelier, Montpelier Station, VAJames Madison / Place of deathJames Madison's Montpelier, located in Orange County, Virginia, was the plantation house of the Madison family, including Founding Father and fourth president of the United States James Madison and his wife, Dolley. Wikipedia
- What did James Madison believe in?
James Madison (1751–1836), the chief author of the Bill of Rights and thus of the First Amendment, was the foremost champion of religious liberty, freedom of speech, and freedom of the press in the Founding Era.
- Who are the 7 founding fathers?
Fact #1: These seven men are the principle Founding Fathers: George Washington, Thomas Jefferson, John Adams, Benjamin Franklin, Alexander Hamilton, John Jay and James Madison. While there were many others who contributed to the founding of the United States, these seven are considered by most as the Founding Fathers.
- Why did some delegates oppose ratifying the Constitution?
The Anti-Federalists opposed the ratification of the 1787 U.S. Constitution because they feared that the new national government would be too powerful and thus threaten individual liberties, given the absence of a bill of rights.
- Why did some of the delegates not endorse the Constitution?
One of the most famous reasons for why certain delegates didn't sign was that the document lacked a legitimate Bill of Rights which would protect the rights of States and the freedom of individuals. Three main advocates of this movement were George Mason, Elbridge Gerry, and Edmund Randolph.
- Why did the delegates decide not to include a bill of rights in the Constitution?
James Madison and other supporters of the Constitution argued that a bill of rights wasn't necessary because - “the government can only exert the powers specified by the Constitution.” But they agreed to consider adding amendments when ratification was in danger in the key state of Massachusetts.
- Why did delegates disagree at the Constitutional Convention?
A central issue at the Convention was whether the federal government or the states would have more power. Many delegates believed that the federal government should be able to overrule state laws, but others feared that a strong federal government would oppress their citizens.
- Which delegates did not want to ratify the Constitution?
Of the 42 delegates still present at the convention when it was finished, 39 signed the Constitution. Only Governor Edmund Randolph (Virginia), George Mason (Virginia), and Elbridge Gerry (Massachusetts) declined to sign.
- Who started American imperialism?
American "Diplomacy"
American imperialism took off from 1900 to 1914 under the leadership of Theodore Roosevelt, William Howard Taft, and Woodrow Wilson.
- Who was the American general who made a plan to rebuild Europe?
In a June 5, 1947, speech to the graduating class at Harvard University, Secretary of State George C. Marshall issued a call for a comprehensive program to rebuild Europe.
- What was in the Marshall Plan?
For the United States, the Marshall Plan provided markets for American goods, created reliable trading partners, and supported the development of stable democratic governments in Western Europe. Congress's approval of the Marshall Plan signaled an extension of the bipartisanship of World War II into the postwar years.
- What prompted the U.S. to create an empire in the late 19 th century?
Both a desire for new markets for its industrial products and a belief in the racial and cultural superiority of Americans motivated the United States' imperial mission.
- What was imperialism in the 20th century?
At the turn of the 20th century, imperialism was well established as a mode of global governance in which a dominant nation exerted control over others through either territorial rule or various forms of economic, cultural, or military influence.
- What time period was the Federalists?
The Federalist Era in American history ran from 1788 to 1800, a time when the Federalist Party and its predecessors were dominant in American politics. During this period, Federalists generally controlled Congress and enjoyed the support of President George Washington and President John Adams.
- What was the federalist era of the Constitution?
After the ratification of the Constitution, a new American government began to take shape in what historians refer to as the Federalist Era. From 1789 to 1801, national leaders grappled with questions relating to implementing the Constitution.
- What time period did the Federalist Papers take place?
On October 27, 1787, the first of the Federalist Papers is published in support of the newly signed Constitution. Between October 1787 and May 1788, Alexander Hamilton, James Madison, and John Jay undertook what was essentially a public relations campaign to encourage New York to ratify the U.S. Constitution.
- What was the time frame of the Federalist Party?
The Federalist Party was a conservative and nationalist American political party and the first political party in the United States. Under Alexander Hamilton, it dominated the national government from 1789 to 1801.
- What was the Federalist era in 1789?
After the ratification of the Constitution, a new American government began to take shape in what historians refer to as the Federalist Era. From 1789 to 1801, national leaders grappled with questions relating to implementing the Constitution.
- What describes a major challenge facing the builders of the Transcontinental Railroad?
Each company faced unprecedented construction problems—mountains, severe weather, and the hostility of Native Americans. On May 10, 1869, in a ceremony at Promontory, Utah, the last rails were laid and the last spike driven.
What is a result of the general acceptance of liberal construction in the united states?
| What was the major challenge during the building of the Central Pacific railroad? | The Central Pacific met its greatest challenge at the outset—the towering Sierra Nevada, which presented enormous engineering obstacles and strangling winter snows. Deep fills, rock cuts, high trestles, snaking grades, and 15 tunnels through 6,213 feet of solid granite blooded the CP crews. |
| What was the most difficult challenge of building the Transcontinental Railroad? | For the US government and the railroad companies, the biggest obstacles in building the Transcontinental Railroad were mountains of solid granite and attacks by Native American war parties. |
| What were the results of the construction of the Transcontinental Railroad? | Just as it opened the markets of the west coast and Asia to the east, it brought products of eastern industry to the growing populace beyond the Mississippi. The railroad ensured a production boom, as industry mined the vast resources of the middle and western continent for use in production. |
| What were the major effects of the Transcontinental Railroad? | Just as it opened the markets of the west coast and Asia to the east, it brought products of eastern industry to the growing populace beyond the Mississippi. The railroad ensured a production boom, as industry mined the vast resources of the middle and western continent for use in production. |
| What proposals represented a loose construction of the Constitution? | The Articles created a loose confederation of sovereign states and a weak central government, leaving most of the power with the state governments. |
| Which group believed in loose construction of the Constitution? | Federalists Federalists favored a strong national government, they believed in loose construction, a broad or flexible interpretation of the Constitution. They hoped to use the new government's powers under the Constitution to unite the quarreling states and keep order among the people. |
| Which president used a loose interpretation of the Constitution? | Alexander Hamilton Alexander Hamilton and his followers favored a loose interpretation of the Constitution, which meant they believed that the document permitted everything that it did not expressly forbid. This contrasted sharply with Thomas Jefferson's strict interpretation. |
| What was the Hamilton plan? | Hamilton's plan called for the government to repay both federal and state debts. He wanted the government to buy up all the bonds issued by both the national and state government before 1789. He then planned to issue new bonds to pay off the old debts. |
| What does following a loose construction of the Constitution mean? | Loose construction is the belief that the Constitution is a dynamic, living document that must change as the nation develops. Loose constructionists do not feel bound by the original intent of the Founding Fathers. They argue that the Founders were practical, pragmatic leaders who did not cast doctrine in concrete. |
| What is a result of the general acceptance of liberal construction in the united states | A strong national government. What is a result of the general acceptance of liberal construction in the United States? A large National government. Where has |
| How did the framers fix the Articles of Confederation? | The Constitutional Convention of 1787 was called to revise the ailing Articles of Confederation. However, the Convention soon abandoned the Articles, drafting a new Constitution with a much stronger national government. Nine states had to approve the Constitution before it could go into effect. |
| Who created the Articles of Confederation? | John Dickinson, a delegate from Delaware, was the principal writer. The Dickinson Draft of the Articles of Confederation named the confederation "the United States of America." After considerable debate and revision, the Second Continental Congress adopted the Articles of Confederation on November 15, 1777. |
| Why did the framers decide to write a new Constitution? | The problems of the national government under the Articles of Confederation led the Founders to decide to write a new constitution. The United States Constitution was written by the delegates who attended the Philadelphia Convention. These delegates are known as the Framers of the Constitution. |
| What was the government formed by the Articles of Confederation best described as? | The Articles created a loose confederation of sovereign states and a weak central government, leaving most of the power with the state governments. The need for a stronger Federal government soon became apparent and eventually led to the Constitutional Convention in 1787. |
| Why did the framers make the articles weak? | The Founders feared giving too much power to a central government, which might become tyrannical. But they overdid it, leaving a central government that could not fund itself, resolve disputes between its component states, or defend the country. |
| What was a Strict Construction of the Constitution? | Strict construction refers to a philosophy of constitutional interpretation that holds that the Constitution should be interpreted and applied based on a precise reading of the text and the text alone. |
| Who was responsible for the creation of the Constitution? | The Constitutional Convention Completes a New Constitution
After five weeks of debate over the committee of detail's draft Constitution, the Constitutional Convention appointed a committee of style to prepare a final version; Gouverneur Morris, later known as the "penman of the Constitution," did most of the work. |
| Who was chosen to oversee the Constitutional Convention? | Presiding Over the Convention: The Indispensable Man. During the spring and sweltering summer of 1787, George Washington provided guidance for 55 state delegates who gathered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania to fiercely debate the future of the United States. |
| Who oversaw the Constitution? | The delegates elected George Washington of Virginia, former commanding general of the Continental Army in the late American Revolutionary War (1775–1783) and proponent of a stronger national government, to become President of the convention. |
| Who was the leader in forming the Constitution? | James Madison, America's fourth President (1809-1817), made a major contribution to the ratification of the Constitution by writing The Federalist Papers, along with Alexander Hamilton and John Jay. In later years, he was referred to as the “Father of the Constitution.” |
| Who helped Thomas Jefferson make the Constitution? | While in Paris before the Constitutional Convention, Jefferson closely followed developments in the United States. He corresponded with individuals who would eventually contribute to the formation of the Constitution, like Madison and John Jay, an author of the Federalist Papers. |
| Why did liberal construction of the Constitution prevail? | What is a reason why liberal construction of the Constitution prevailed? wars and economic crises called for national action, spectacular advances in transportation and communication impacted the scope of the government, the people themselves demanded more and more services from government. |
- What is a liberal constructionist in government?
Liberal constructionists believe that, when interpreting the Constitution, meaning and intent should be inferred based on consideration of the document as a whole. Strict constructionists, on the other hand, take a literal interpretation of the Constitution and apply it to the law.
- Which of the following has been a value of liberal constructionists?
Which of the following has been a value of the liberal constructionists? The Constitution must be interpreted broadly, with an eye toward change.
- What is liberal construction of the Constitution?
Liberal constructionists believe that, when interpreting the Constitution, meaning and intent should be inferred based on consideration of the document as a whole. Strict constructionists, on the other hand, take a literal interpretation of the Constitution and apply it to the law.
- What Committee was appointed at the Constitutional Convention?
A Committee of Eleven (also called the Grand Committee), appointed on July 2, proposed a solution to an impasse over representation in the House and Senate. On August 6 a Committee of Detail produced a draft Constitution that summarized the principles already agreed upon by the Convention.
- What did Jefferson do that was a strict interpretation of the Constitution?
Jefferson took a strict, literal view of constitutional powers, meaning that specific powers reserved for the President and Executive Branch needed to be spelled out in the Constitution.
- Why did Jefferson reverse the policies of the previous administration?
Jefferson and his allies sought to reverse the Judiciary Act of 1801, partly because they did not believe the new judicial positions were necessary, and partly to weaken Federalist influence on the courts.
- How did Thomas Jefferson oppose the Constitution?
Thomas Jefferson's December 20, 1787, letter to James Madison contains objections to key parts of the new Federal Constitution. Primarily, Jefferson noted the absence of a bill of rights and the failure to provide for rotation in office or term limits, particularly for the chief executive.
- What was a result of Jefferson's strict interpretation of the Constitution?
- Limiting the federal government flowed from his strict interpretation of the Constitution. Finally, Jefferson also committed his presidency to the protection of civil liberties and minority rights.
- Did Jefferson believe in a strict construction view of the Constitution?
- President Jefferson believed in a strict construction of the US Constitution — unless the Constitution specifically granted a power to the government, the power belonged to the people.
- What were the delegates afraid of?
Many delegates believed that the federal government should be able to overrule state laws, but others feared that a strong federal government would oppress their citizens. The delegates compromised by allotting specific responsibilities to the federal government while delegating all other functions to the states.
- What did some of the framers of the Constitution fear might happen if they did not include a Bill of rights?
The Federalists opposed including a bill of rights on the ground that it was unnecessary. The Anti-Federalists, who were afraid of a strong centralized government, refused to support the Constitution without one.
- What are the two main issues the delegates arguing about?
In May, 55 delegates came to Philadelphia, and the Constitutional Convention began. Debates erupted over representation in Congress, over slavery, and over the new executive branch.
- Why did some delegates dislike the Constitution?
The Anti-Federalists opposed the ratification of the 1787 U.S. Constitution because they feared that the new national government would be too powerful and thus threaten individual liberties, given the absence of a bill of rights.
- What fears did delegates from small states have?
Small states feared they would be ignored if representation was based on population while large states believed that their larger populations deserved more of a voice. Under the bicameral system, each party would be represented in a balance of power.
- Who started the Marshall Plan?
President Truman
On April 3, 1948, President Truman signed the Economic Recovery Act of 1948. It became known as the Marshall Plan, named for Secretary of State George Marshall, who in 1947 proposed that the United States provide economic assistance to restore the economic infrastructure of postwar Europe.
- What was the name of the plan that became known as the Marshall Plan?
The Marshall Plan was a U.S.-sponsored program designed to rehabilitate the economies of 17 western and southern European countries in order to create stable conditions in which democratic institutions could survive in the aftermath of World War II. It was formally called the European Recovery Program.
- What is the Global Marshall Plan?
The goal of the Global Marshall Plan Initiative is to establish a framework compatible with sustainability for the global economy – a global Eco-Social Market Economy.
- Who was the United States president who planned to win the war in Europe?
President Woodrow Wilson wanted the United States to help keep the peace in Europe, but the US Congress blocked his attempt to have America join the recently created League of Nations.
- What do liberal constructionists believe about the Constitution?
Liberal constructionists believe that, when interpreting the Constitution, meaning and intent should be inferred based on consideration of the document as a whole. Strict constructionists, on the other hand, take a literal interpretation of the Constitution and apply it to the law.
- What are the differences between strict construction and liberal construction positions on the scope of congressional power?
1. Strict constructionists believed that Congress should exercise only its expressed powers and those powers absolutely necessary to carry out those expressed powers. 2 Liberal constructionists hesitated to use implied powers. 3.
- What did liberal constructionists believe Congress should be able to do?
Hamilton & the liberal constructionists believed the Necessary & Proper Clause gave them the power to do whatever was necessary to carry out the expressed powers. Specifically, they wanted to set up a National Bank to manage the currency and finances of the nation.

